Cognitive Artificial Intelligence: it’s free decision-making
Artificial Intelligence does a lot of stuff for us. Kind of.
Coming up with a technology that can perform autonomous data processing, extract value out of it, and offer solutions was a major breakthrough. It allowed people to apply it to the most mundane analysis of large amounts of data.
Now we have AI analyzing our likes and recommending content and products to us. It predicts the best routes for trips, analyzes equipment performance, and a bunch of other useful things.
But like all things, AI isn’t perfect. It can be more perfect-er, though.
The key to that is in constant development and advancement.
At the end of the day, AI is about recognizing patterns, but we need it to be more like a human.
Let’s find out how Cognitive Artificial Intelligence works.
Defining Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Computing
Folks less familiar with the terms often confuse AI with Cognitive Computing and vice versa. How are those related to each other? Are there any differences between the two?
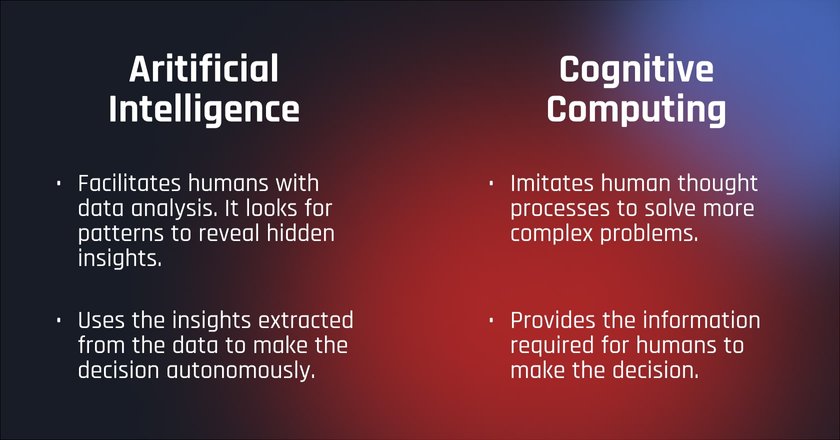
So, Artificial Intelligence is a set of technologies that aim at facilitating human productivity with automated data processing. It recognizes patterns in the data to help find solutions to problems.
On the other end of the table, we have Cognitive Computing. That is a subset of AI that is striving to imitate the human thought process to solve more complex problems. The technology under the hood imitates human reasoning to work with incomplete sets of data and deal with non-typical situations.
And there are key attributes that facilitate the effectiveness of Cognitive Computing:
- Adaptiveness. The technology works with constantly changing sets of information.
- Interactivity. The system’s user can interact with it as their needs change.
- Iteration and statefulness. The tech can pull additional information if it lacks the resources to solve the problem.
- Contextuality. The thing that separates Cognitive Computing from AI the most: cognitive tech makes use of the contextual data to facilitate its analysis. It can consider syntax, time, location, domain, requirements, and other info.
So, that’s the main thing that differentiates AI from Cognitive Computing. While AI is basically a supercharged data analytics system that can also offer decisions based on that analysis, Cognitive Computing goes beyond that and simulates the way human brains work to work with irregular situations.
Summing up the differences, here’s what we get:
The problem with Artificial Intelligence
So, to the part where I said that Artificial Intelligence is not perfect.
It can be, but it’s not.
What’s its problem then?
And then there are TV shows. As it appears, people do like to know more about the creative process of their favorite series: cast Since we’re doing that media & entertainment thingy with technology, let’s see the reasons AI lags behind in terms of video analysis.
The major problem with Artificial Intelligence is that it isn’t flexible enough to work with ever-changing datasets.
For example, you need to create a trailer for a certain episode of a TV show, or make a highlight reel for a sporting event.

We’re assuming that a manual approach is not an option because of the scale of content, so automation is the way to go here.
If you’re using AI to cut your clips, you will have to dedicate some time to training the technology to recognize things you need. And that before the entire ordeal begins.
Learn about more effective ways to automate content production.
Oh, and what things you may need the AI to recognize?
Best moments of the footage, of course?
But what is that exactly? How can AI tell the difference between a tense moment and a quip?
The truth is — it can’t. So, you go for the workarounds.
For instance, with sporting events, you can train AI to detect certain audio and visual clues — like the crowd cheering or the ball hitting the basket. That certainly means a score, so it is a good highlight.
But what about such sports as golf or swimming? Not much cheering going on there, is it?
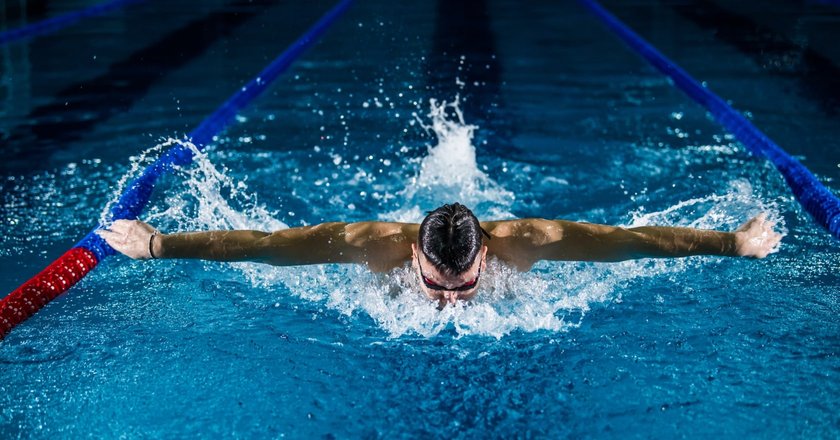

Unfortunately, there’s not much you can do in that sort of situation. AI lacks the ability to understand the context of the footage to kind of “feel” the intensity of the particular moment.
It can automate face recognition, but cannot tell apart main characters from secondary ones.
Cognitive Artificial Intelligence is the way
In order to grasp contextual information, we need to use Cognitive Computing capabilities. Human-like reasoning helps the machine to understand the context of what they’re dealing with, improving the results.
And we already have technology that does this.
Meet Cognitive AI — the next stage of Artificial Intelligence development meant to draw the gap between human and machine intelligence.
The tech baked into that allows Cognitive AI to make decisions in unpredictable environments, making use of both structured and unstructured data.
Missing information ceases to be the deal breaker as well — Cognitive AI pulls the information from previous analyses to facilitate its decision-making.
Cognitive AI and video content analysis
Let’s get back to our case of video content analysis with the help of AI. And switch AI with Cognitive AI.
Here’s what we get.
When working with video, Cognitive AI can actually understand what’s going on the screen, and it uses that information to draw better conclusions.
With such tools as deep learning, digital image processing, and computer vision, Cognitive AI can imitate the way humans perceive things.
And then, facilitating the decision, it applies probabilistic AI, cognitive science, machine perception, and math modeling.
So it doesn’t just catch the ball going into the goal area. It can tell apart a game-breaking penalty, last-second touchdown, and all things of that sort thanks to contextual understanding of the content.
Discover the potential of Cognitive Computing!
It doesn’t just recognize faces of people appearing in the footage. It can tell which ones are important to the context of the video, and which ones are secondary in that regard.

Should you make it crop the video from landscape to portrait aspect ratio — Cognitive AI will make sure that the most important part of the scene stays within the vertical frame.
So, you know, your viewers on TikTok won’t be staring at a portion of a background.
The bottom line is that it understands the content it analyzes. So, whether it is video summarization, nudity detection, or else — with some tweaking, it can do it all.
Artificial Intelligence, but more intelligent
The creation of AI has really turned things around for technology augmenting our lives — it made effective automation of all kinds of actions possible.
The tech that learns as it analyzes more and more stuff? Great success!
But despite its reputation, it has a lot of limitations that keep it from automating complex tasks effectively.
Basic AI can make decisions with incomplete data, can’t contextually understand the content it works with. In basic terms, it fails to reason as humans do.
On the other hand, we have Cognitive Computing — a set of technology that can imitate human cognitive features to some extent.
Share you thoughts and ideas with us!
You know what has to be done to overcome their respective shortcomings, right?
We combine the both and get Cognitive AI — the perfect intelligence serum that dwarfs the capabilities of its predecessors.
Looking to apply Cognitive AI to automated video analysis? Great! Reach us at support@cognitivemill.com or fill in the form below. We will be happy to chat!