Human augmentation in media and entertainment

Technology is now making humans more capable than ever — in terms of their physical, psychological, and social abilities.
But no Terminator stuff. At least for now.
Tech innovators focus on enhancing human strengths and optimizing weaknesses. Let’s see what’s that all about — and how the media and entertainment industry can benefit from it.
What is human augmentation?
Before we give a clear human augmentation definition, the one thing to know is that the idea is not new.
We have been doing this for a long time now. Can’t see that well? You can wear glasses or contacts. Looking to conquer space? Get in the spacesuit. Struggling to remember stuff? There’s an app for that.
The concept behind all of those developments — human augmentation — aims at perfecting and improving what a human body and mind can do to enhance our day to day lives.
And who knows what the future can bring: maybe in the future we will be able to carry the groceries from our cars inside the house in one trip.

But let’s not get ahead of ourselves here. Let’s try to see where human augmentation technology can help us at that point.
As of now, human augmentation covers two major areas: human performance optimization and enhancement.
Human performance optimization
That branch of human augmentation relies on technology to push the abilities of the human body to its highest peaks. We can further divide innovations in that branch into two major spheres:
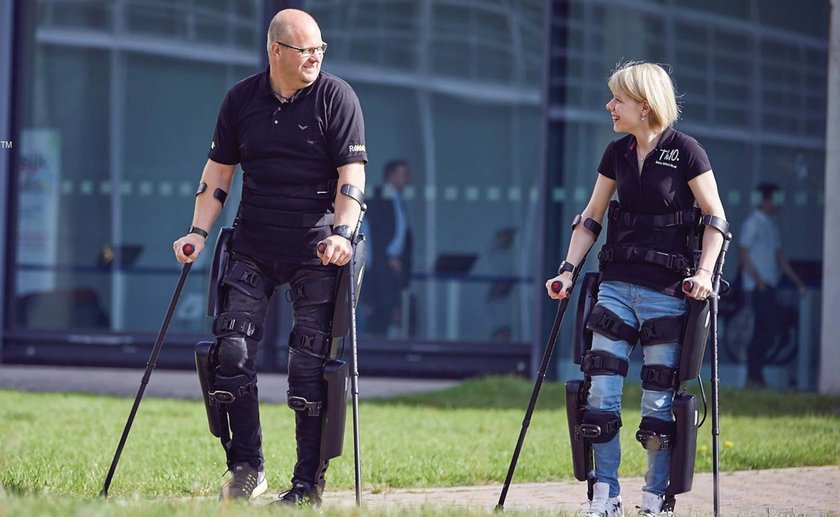
- Replication — technology restores the compromised human ability. Some time ago we had prosthetics that only replaced lost body parts to a limited extent but now can replicate such nuanced parts as fingers. There are also exo-skeletons that can help disabled persons walk;

- Supplementation — aims at adding more potential to an individual capacity. For instance, Augmented Reality devices and smart wearables allow us to get relevant information and communicate more effectively.
Human performance enhancement
Enhancement is where we go up a notch with human augmentation technology. It is all about addition and enhancement of new abilities beyond what a human body can do.
- Excess — that includes human augmentation projects with the goal of exceeding human potential. We can take Neuralink as a great example: an interface allows the human brain to communicate with a computer.
Pushing far beyond the limits of the human mind and body covers many aspects of said field. We can divide it into three major areas of human enhancement targeted by technology:
Let us know what you think!
- Physical ability — human body strength, speed, agility and endurance;
- Psychological ability — human emotions, cognitive abilities, attention, and memory;
- Social activity — humans’ ability to act as a group and interact with each other.
As for now, physical ability enhancement is the biggest area of interest for the human augmentation market:
- Folks in British military are testing jetpacks and exo-skeletons;
- Athletes get their hands on gear that drastically improves their performance;
- Some are even taking over the evolution process: what do you think about having a third thumb?

So, let's see how things are going there in terms of technology being applied.
Technology at the core of human augmentation
The third thumb can’t be the answer to all problems, no matter how bad I want it to. So, human augmentation companies are looking into all kinds of technology to help enhance all aspects of our lives. Let’s see what the most prominent ones are.
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering opens the door for precision medicine — the concept which is based on genetic characteristics of each individual. Information on genes can be used to treat humans more efficiently with individual features of each case in mind.
Bioinformatics
A level below precision medicine, bioinformatics analyzes molecular and biological data to understand the influence of different kinds of treatments on the human body.
Neural interfaces
That’s where such tech as the Neuralink steps in. Human augmentation industry builds systems that can enable the human brain to talk to computers. For instance, that human augmentation technology can enable better control over prosthetics.

Pharmaceuticals
It is not only about treating coughs and headaches. Companies have been developing drugs that can temporarily improve the physical, psychological, and cognitive abilities of humans: those can help remember things better, grow muscles quicker, be more focused, and so on.
At the moment, the development of the human augmentation market in the pharmaceuticals field faces issues of side-effects that the drugs have on those taking them.
So, the goal for the near future is to address that.
I hope they are also looking into those Matrix pills. I would like to try some. Email me if you have any info on that.
AI and cognitive computing
Artificial Intelligence targets the cognitive abilities of humans, trying to replicate and even surpass them to the largest extent.
It is not a direct way of augmenting human intelligence: rather than “thinking differently” it is about “making the machine think much more quickly and effectively for you”. Which is very convenient in many areas of human activity that involve dealing with large volumes of information.
Instead of having humans slaving away in front of bottomless spreadsheets we can now have a technology that not only goes through the information, but can act upon it.
Need to optimize your production with automation?
It can carry out analysis and recognize patterns, and use that knowledge to make predictions.
To demonstrate how AI human augmentation works, we’ll take manufacturing as an example: let’s say we are dealing with maintenance scheduling at a production facility. We can spare the engineers the mundane inspections and have devices that monitor the equipment condition.
The AI system then analyzes the condition data and decides whether a particular piece of equipment is due for maintenance.

And then there’s decision making. That aspect is covered by cognitive computing technology, which pushes human augmentation even further.
The deal is the same as with AI: it helps humans save resources by analyzing stuff more effectively. The major difference is that while AI can do a lot in terms of structuring the data, its usefulness decreases significantly if the data we’re working with isn’t complete.
Cognitive computing tech is more than capable of handling incomplete data sets. And what’s more — it can make decisions based on the data.
So, let’s see how all that AI human augmentation stuff happens, taking the media and entertainment industry as an example.
Human augmentation in media and entertainment
We start off by establishing what actually needs to be augmented here. With the media and entertainment industry, effective content production is the top priority.
Here’s our target: AI human augmentation can help companies generate content more effectively, with less effort and time spent on mundane tasks.
Obviously, we are not talking about using tech to make movies and stuff: the large portion of the effort there is fueled by human creativity, augmenting which still lacks required consistency.

But what about more down to the ground tasks — cutting the trailers, highlights, making compilations and so on?
It’s pretty much manual work for the most part: a team of editors gets sporting event footage, a movie, or any other video content. The go through it and cut whatever content they need:
Share your ideas! We would love to help you improve.
- Edit the most tense moments for the trailer or a commercial;
- Cut high drama sequences for a highlight compilation;
- Crop the content to better fit mobile-oriented social media platforms;
- Edit out or filter unwanted content: disturbing imagery of nudity.
That part of the work is crucial because it helps companies develop their brands, reach new audiences, and further promote the content they produce.
But that part of the work is also countless hours in front of the screens.
And those hours can be trimmed down significantly with the help of cognitive computing. Human augmentation tech can take over the mundane parts of the production process to speed things up.
Some media companies are already implementing Artificial Intelligence to provide assistance for editors. But the problem is that regular AI might not be enough.
For example, a streaming or an OTT platform has a movie coming in for release. Before the user can watch it, we have to make some adjustments to improve the viewing experience.
Let’s say the editor has to go through the footage and edit the unwanted content, and mark the opening and ending credits so the folks on their couches could skip those.
Here’s how it goes.
- The editor looks through the entire movie;
- He marks the parts with unwanted content;
- He goes through credits to make sure there are no scenes during the credits;
- He marks the credits apart from those containing important story moments;
- Then the team edits out the content and uses the data to place the buttons suggesting to skip the credits.
Real fun, right?
And we are not talking about generating trailers or marking cast members. That would only add to the eternity those people have to spend working on simple tasks.
Artificial Intelligence is able to solve the problems to some extent. But it is only good for automatically tagging the required types of content.
Let's automate your production process!
So, returning to our example, AI could tag the inappropriate content, but the editor still has to go in and manually edit it out.
That approach lacks decision-making aspects that could optimize the production process even further. So much for the human augmentation part.
But there is a technology that has those aspects over AI — cognitive computing.
At AIHunters, we rely on cognitive computing that leverages tech to imitate the way the human brain works. That opens the opportunity for a much deeper and comprehensive industry automation.
Cognitive computing augments the editor's bandwidth with human-like analysis, allowing them to dedicate less resources towards routine tasks and focus on more complex work with such tech as:
- Machine perception;
- Probabilistic AI;
- Cognitive neurodynamics;
- Brain-inspired computer vision.
It is able to draw informed decisions based on incomplete data sets, which is nowhere near the possibilities of regular AI.
CognitiveMill™, being based on a cognitive computing cloud platform, can not only analyze the video content, but actually make sense of it.
Say we have a simple task of making a highlight compilation of a sporting event. A regular AI system can rely on markers pre-placed by scouts from the field, find the markers, and cut the scenes.
Other approaches may include an audio analysis: the system tries to identify the crowd reacting to certain in-game moments and judge whether those are highlight-worthy.
But cognitive computing does not need any of that. Human-like comprehension allows for understanding the context of the video content that results in quick and precise results. Relying on the footage alone, the system consistently produces highlight compilations.
Making sense of the footage goes a long way as well.
Need a high drama moment, a goal compilation, or mascot dance video? Better get to re-training your AI.
CognitiveMill™, on the other hand, needs no training. Just roll the clip, get the results, go on with your day.
Cognitive computing can also do a ton of other stuff with video, such as:
- Identifying cast members appearing on the screen and telling main and side characters apart;
- Recognizing nudity and other inappropriate content and blurring it out;
- Making movie or TV show trailers automatically;
- Smart ad insertion based on context of the video;
- Cropping the footage to a portrait aspect ratio for mobile-oriented social media;
Advanced methods of video analysis also enable CognitiveMill™ to work with content of any genre. It effectively chews through movies, TV series, comedy specials, talk shows, animation, sporting events, and content generated by the users on the internet.
With Artificial Intelligence, you would have to spend lots of time training the algorithm on a particular content type. Doesn’t really augment human effort, does it?
Explore human augmentation prospects in media and entertainment
Human augmentation aims at optimizing and even surpassing the effectiveness of human effort in all spheres of our lives.
From the media and entertainment perspective, CognitiveMill™ can even replace the human editor entirely. That includes more straightforward video production processes like celebrity or end-credits recognition.
When it comes to more complex tasks, the rate of human augmentation reaches up to 80% of business cases.
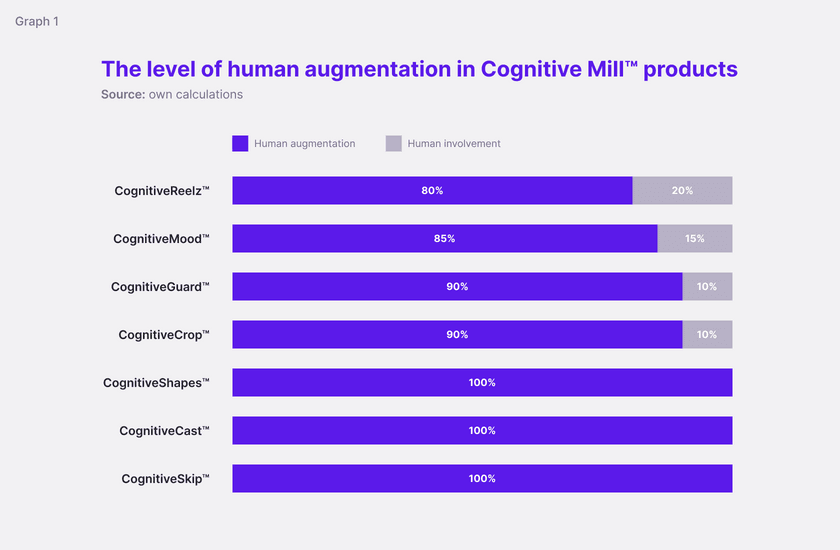
That’s what you get: up to 80% of tasks can be done by a robot. You can have your staff doing more demanding and creative tasks, improving the efficiency of your business.
Looking to find out how cognitive computing can help your media business? Drop us a line at support@cognitivemill.com or fill in the contact form below. We will be thrilled to explore your case and offer a solution!